
Hemorrhoids (piles) are vascular structures in the anal canal. In their normal state, they are cushions that help with stool control and protect anal sphincter. They become a disease when swollen or inflamed.
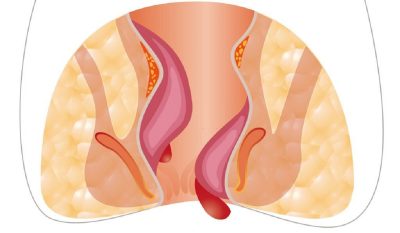
TWO TYPES OF HEMORRHOID
- External hemorrhoids are outside the anus and cause lumps to protrude through the anus. The symptoms are pain and swelling in anal area.
- Internal hemorrhoids are inside the anus (the opening to the back passage), usually present with bright red rectal bleeding.
- First stage: they cannot be seen or felt.
- Second stage: they prolapse out of the anal canal during a bowel movement and retract back inside after that.
- Third stage: they prolapse but do not retract by their own. You need to push them back inside.
- Fourth stage: they cannot be retracted anymore, become swollen and painful.
CAUSE
- Hemorrhoids are mostly caused by inappropriate bowel movement i.e. too much/too long straining or too hurry which cause pressure on the rectum.
- Hardened feces causing rectal bleeding.
- Constipation or chronic diarrhea.
- Pregnancy.
SYMPTOMS
- Fresh blood during bowel movement.
- You might feel the lump because the swollen veins are prolapsing.
- Itchy around the anus.
- Painful around the anus because the thrombosis in the veins causes them to enlarge (it is called thrombosed external hemorrhoids).
- Prolonged bleeding could cause blood loss, anemia, faint, or dizziness.
DIAGNOSIS
If you notice fresh blood during bowel movement, please see the doctor to make sure it is not something serious like cancer or other digestive tract related diseases. Your doctor will check your anus with gloved fingers and/or invasive instrument. In some cases colonoscopy might be needed to make decision on the best and most appropriate treatment.
TREATMENT
- Non-surgical treatment
- Eat fiber rich food and drink lots of fluid to soften stools and avoid too much straining during bowel movement.
- Use suppository after bowel movement or shower. Suppository is now available in form of cream to apply on the external type.
- Using a type of rubber band to tie off the hemorrhoid and restrict blood flow to it. The hemorrhoid will then slowly shrink and disappear within 5-10 days. This method is effective when the hemorrhoid is small or medium and external.
- The doctor may inject medicine around the blood vessels to cause the hemorrhoid to shrink.
- Electricity, lasers, heat, or cold is recommended for small size of hemorrhoids.
- Surgical treatment is the last treatment option if other options are not effective or in severe cases or the last stages of hemorrhoids i.e. stage 3 or 4 (external, inflamed). However, it gives the quickest result of treatment.
COMPLICATIONS
- Prolonged blood loss can cause anemia.
PREVENTION
- Change your eating habits to prevent stool from being too hard so it is easier to pass without straining and without putting pressure on the veins of the anal canal.
- Go to toilet as soon as you feel the urgency, try to schedule your bowel movement and do not strain too much.
- Avoid sitting on the toilet for too long.
- Avoid constipation by moving your body, whether by walking or exercising. This will make it more comfortable to have bowel movements.
- Eat foods that are high in fiber, such as fruit, leafy vegetables, and grains.
- Drink at least 6-8 glasses of water each day. Avoid alcohol.
